Querying relational Databases: PostgreSQL
- PostgreSQL
- Spin and Fermyon Wasm Functions
- Using Spin Application Templates
- Creating Our New Spin Application
- Configuration
- Implementing the Spin Application
- Compiling the Spin Application
- Running the Spin Application Locally
- Deploy to Fermyon Wasm Functions
PostgreSQL
PostgreSQL, is a powerful, open-source object-relational database system that has earned a strong reputation for reliability, robustness and performance. This tutorial will implement a persistent storage solution for Fermyon Wasm Functions, using PostgreSQL. In this tutorial, we will be using NEON’s free PostgreSQL service.
Provisioning the Database and Seeding Sample Data
Once you’ve created a free account with NEON, you’re asked to create a project, you can customize the settings to your needs and confirm the recommended horizontal scaling settings.
With your free project being created, find the SQL Editor and run the following SQL commands to provision the Products table and to seed some sample data:
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS Products (
Id varchar(36) PRIMARY KEY,
Name TEXT NOT NULL,
Price DOUBLE PRECISION);
INSERT INTO Products (Id, Name, Price)
SELECT 'faac630e-a645-4459-9d7e-751df4016a6e', 'V-Neck T-Shirt', 19.99
WHERE NOT EXISTS (SELECT Id FROM Products WHERE Id = 'faac630e-a645-4459-9d7e-751df4016a6e');
INSERT INTO Products (Id, Name, Price)
SELECT 'c01dce8a-3a50-4ef6-a0f1-7f9f48a238c8', 'Hoodie with Logo', 79.99
WHERE NOT EXISTS (SELECT Id FROM Products WHERE Id = 'c01dce8a-3a50-4ef6-a0f1-7f9f48a238c8');
INSERT INTO Products (Id, Name, Price)
SELECT '6f062dc2-bbf2-4c6c-8169-3511462cd54b', 'Belt', 14.99
WHERE NOT EXISTS (SELECT Id FROM Products WHERE Id = '6f062dc2-bbf2-4c6c-8169-3511462cd54b');
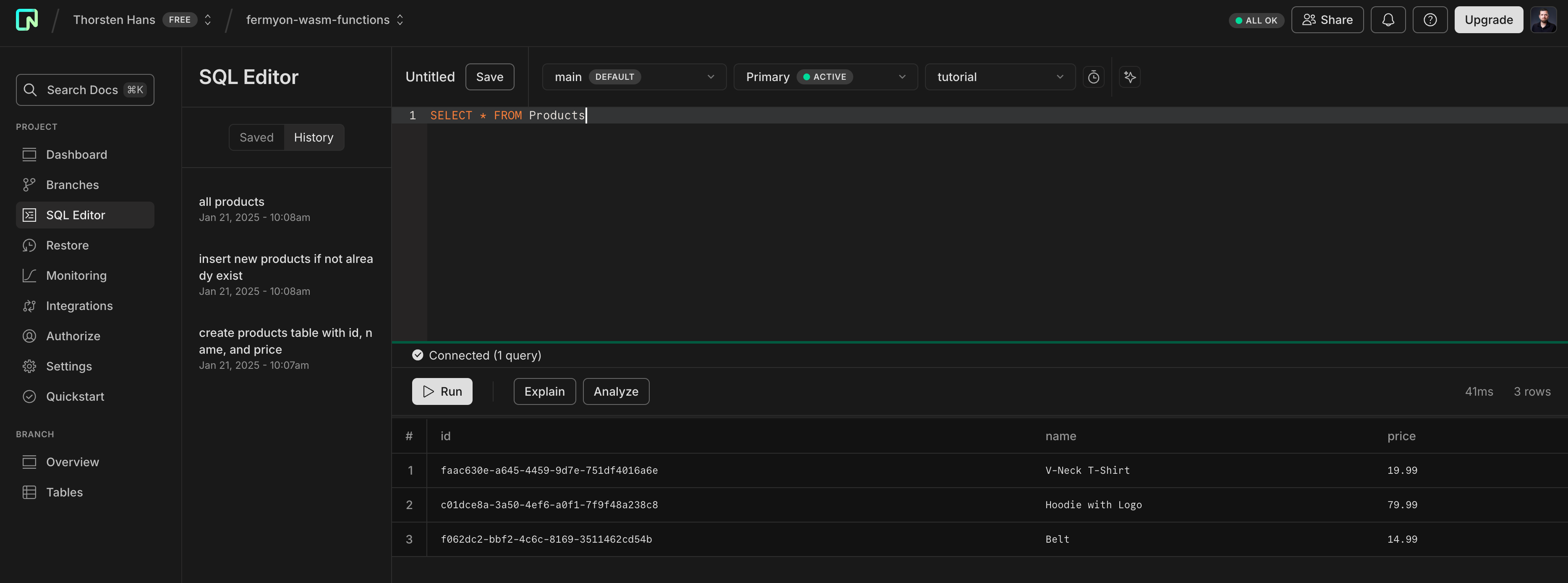
Once you’ve executed the SQL statements from above, you can run a SELECT * FROM Products to verify your database setup. NEON’s SQL Editor should render the table contents as shown in the following figure:
You can find the connection string for your PostgreSQL database from NEON’s cloud portal as well. Navigate to the project dashboard and note the connection string, we’ll need it for deploying the application to Fermyon Wasm Functions.
Spin and Fermyon Wasm Functions
First, you need to have spin CLI installed on your computer. Please use the official Fermyon Wasm Functions Quickstart to both install Spin and also log in to Fermyon Wasm Functions.
Using Spin Application Templates
The spin CLI facilitates the creation of new Spin applications through the use of application templates. You can install Spin application templates using the official Spin CLI documentation. The template we are interested in, for this tutorial, is the http-js template.
Creating Our New Spin Application
The official spin CLI documentation also has instructions on how to create a new Spin application, from an existing template. Using the docs as a reference, we can create a new Spin application based on the http-js template, move into the application directory and install its dependencies as shown here:
$ spin new -t http-js -a hello-postgresql
$ cd hello-postgresql
$ npm install
Configuration
Open the Spin application’s spin.toml file, add an application variable and link it to the hello-postgresql component. This allows modifying the connection string for PostgreSQL without changing the actual source code. Consult the Spin documentation to learn more about using variables in Spin.
[variables]
pg_connection_string = { required = true}
[component.hello-postgresql.variables]
pg_connection_string = "{{ pg_connection_string }}"
You will also need to explicitly add the address of your PostgreSQL endpoint to the manifest, so that the Wasm component is allowed to send network requests to it. See the following example, that defines the allowed_outbound_hosts property within the component configuration ([component.hello-postgresql]) section.
Caution: Please recognize that for outbound connectivity we must specify the protocol to be
postgres://and explicitly add the PostgreSQL default port (5432) as shown here:
[component.hello-postgresql]
source = "target/hello-postgresql.wasm"
allowed_outbound_hosts = [
"postgres://ep-bread-garden-11223344.eu-central-1.aws.neon.tech:5432",
]
Implementing the Spin Application
The application we’re going to implement will provide common CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations to interact with products stored in PostgreSQL using HTTP requests. Besides Spin SDK for JavaScript, our application will also use the uuid package as a dependency. To install it, execute the following command from within the application directory:
$ npm install @spinframework/spin-postgres @spinframework/spin-variables uuid
Note: The above npm install command installs the default packages in the template as well as the @spinframework/spin-mysql and @spinframework/spin-variables required for this tutorial.
Note: For the sake of simplicity, we will place all JavaScript code in the
index.jsfile generated byspin new. Delete its contents and keep on appending the JavaScript snippets shown as part of this tutorial.
We’ll start with importing necessary capabilities, defining application constants, two helper functions, and laying out the HTTP API of our Spin application using the AutoRouter provided by the itty-router module (which is specified as dependency of the app):
import * as Variables from "@spinframework/spin-variables";
import * as Postgres from "@spinframework/spin-postgres";
import { AutoRouter } from "itty-router";
import { v4 as uuidv4 } from 'uuid';
import { validate as uuidValidate } from 'uuid';
const router = AutoRouter();
const decoder = new TextDecoder();
// define application constants
const SQL_CREATE = "INSERT INTO Products (Id, Name, Price) VALUES ($1, $2, $3)";
const SQL_READ_ALL = "SELECT Id, Name, Price from Products ORDER BY Name";
const SQL_READ_BY_ID = "SELECT Id, Name, Price from Products WHERE Id = $1";
const SQL_UPDATE_BY_ID = "UPDATE Products SET Name = $1, Price = $2 WHERE Id = $3";
const SQL_DELETE_BY_ID = "DELETE FROM Products WHERE Id = $1";
const DEFAULT_HEADERS = {
"content-type": "application/json"
};
// helper function to quickly respond with an HTTP 400
function badRequest(message) {
return new Response(JSON.stringify({ message }), { status: 400, headers: DEFAULT_HEADERS });
}
// helper function to quickly respond with a 404
function notFound(message) {
return new Response(JSON.stringify({ message }), { status: 404, headers: DEFAULT_HEADERS });
}
// Layout the HTTP API
router
// C(reate) -> Add a new product
.post("/products", async (request, { connectionString }) => createProduct(await request.arrayBuffer(), connectionString))
// R(ead) -> Read all products
.get("/products", async (_, { connectionString }) => readAllProducts(connectionString))
// R(ead) -> Read a single product using its identifier
.get("/products/:id", async ({ params }, { connectionString }) => readProductById(params.id, connectionString))
// U(pdate) -> Update a product using its identifier
.put("/products/:id", async (request, { connectionString }) => updateProductById(request.params.id, await request.arrayBuffer(), connectionString))
// D(elete) -> Delete a product using its identifier
.delete("/products/:id", async ({ params }, { connectionString }) => deleteProductById(params.id, connectionString))
.all("*", () => notFound("Endpoint not found"));
// Spin application entry point
addEventListener('fetch', async (event) => {
// if the connection string is not set, return early with a HTTP 500
const connectionString = Variables.get("pg_connection_string");
if (!connectionString) {
event.respondWith(new Response(
JSON.stringify({ message: "Connection String not specified" }),
{ status: 500, headers: DEFAULT_HEADERS }
));
}
// Let the HTTP router handle incoming requests
// pass the connection string as extra
event.respondWith(router.fetch(event.request, { connectionString }));
});
Implementing the Create Handler
With the design of the HTTP API in place, we could move on and start implementing the different scenarios. First, let’s start by implementing the createProduct function, which is responsible for persisting new products in the PostgreSQL database using Postgres APIs provided through the Spin SDK for JavaScript:
function createProduct(requestBody, connectionString) {
// validate the request payload
let payload = JSON.parse(decoder.decode(requestBody));
// if payload does not match the expectations, return early by sending an HTTP 400
if (!payload || !payload.name || typeof payload.price != "number") {
return badRequest("Invalid payload received. Expecting {\"name\":\"some name\", \"price\": 9.99}");
}
// construct a new Product using user provided data and
// by rolling a new UUID
const newProduct = {
id: uuidv4(),
name: payload.name,
price: payload.price
};
// Open the PostgreSQL connection
const connection = Postgres.open(connectionString);
// Persist the new product in database
connection.execute(SQL_CREATE, [newProduct.id, newProduct.name, newProduct.price]);
// Create an HTTP 201 (Created) response
let customHeaders = {
"Location": `/products/${newProduct.id}`
};
Object.assign(customHeaders, DEFAULT_HEADERS);
return new Response(JSON.stringify(newProduct), { status: 201, headers: customHeaders });
}
Implementing the Read Handlers
Our Spin application has two different handlers for reading data. The readAllProducts is responsible for returning the list of all products from the PostgreSQL database, whereas the readProductById is used to retrieve a single product from the database using its identifier. Let’s start by looking at the readAllProducts function:
function readAllProducts(connectionString) {
// open PostgreSQL connection
const connection = Postgres.open(connectionString);
// load all products from the database
let result = connection.query(SQL_READ_ALL, []);
// iterate over each row received
let items = result.rows.map(row => {
// and construct a JavaScript object containing the data of a particular product
return {
id: row["id"],
name: row["name"],
price: +row["price"]
};
});
// Create an HTTP response with status code 200
return new Response(JSON.stringify(items), { status: 200, headers: DEFAULT_HEADERS });
}
In contrast, the readProductById handler, validates potential UUIDs provided by the corresponding route parameter. If a request was sent to the API with a mal-formatted UUID, the request will be terminated early and an HTTP 400 (Bad Request) is returned to the callee:
function readProductById(id, connectionString) {
// validate UUID
if (!uuidValidate(id)) {
return badRequest("Invalid identifier received via URL");
}
// open PostgreSQL connection
let connection = Postgres.open(connectionString);
// retrieve a product using its identifier
let result = connection.query(SQL_READ_BY_ID, [id]);
// if we receive 0 rows, respond to the request with an HTTP 404 (Not Found)
if (result.rows.length == 0) {
return notFound("Product not found");
}
let found = {
id: result.rows[0]["id"],
name: result.rows[0]["name"],
price: +result.rows[0]["price"]
};
// Create an HTTP 200 response
return new Response(JSON.stringify(found), { status: 200, headers: DEFAULT_HEADERS });
}
Implementing the Update Handler
Next on our list is updating an existing product in the database. Again, we’ll take the product identifier from the corresponding route parameter. Additionally, we pass the request payload into the updateProductById, which we’ll use to update individual properties of the product in the database.
function updateProductById(id, requestBody, connectionString) {
// validate UUID
if (!uuidValidate(id)) {
return badRequest("Invalid identifier received via URL");
}
// validate the payload
let payload = JSON.parse(decoder.decode(requestBody));
if (!payload || !payload.name || typeof payload.price != "number") {
return badRequest("Invalid payload received. Expecting {\"name\":\"some name\", \"price\": 9.99}");
}
// construct the updated product
const product = {
id: id,
name: payload.name,
price: payload.price
};
// open PostgreSQL connection
const connection = Postgres.open(connectionString);
const updatedRows = connection.execute(SQL_UPDATE_BY_ID, [product.name, product.price, product.id]);
// if update did not affect any rows, return a not found
if (updatedRows == 0) {
return notFound("Product not found");
}
// construct a HTTP 200 response
let customHeaders = {
"Location": `/items/${id}`
}
Object.assign(customHeaders, DEFAULT_HEADERS);
return new Response(JSON.stringify(product), { status: 200, headers: customHeaders });
}
Implementing the Delete Handler
Last, but not least let’s take care of deleting a product from the PostgreSQL database. The deleteProductById function takes the product identifier from the route parameter, validates it and tries to delete the product from the database. If no rows were affected from the delete operation, we will again return an HTTP 404 (Not Found), otherwise we respond with a 204 (No Content):
function deleteProductById(id, connectionString) {
// validate UUID
if (!uuidValidate(id)) {
return badRequest("Invalid identifier received via URL");
}
// open PostgreSQL connection
const connection = Postgres.open(connectionString);
const deletedRows = connection.execute(SQL_DELETE_BY_ID, [id]);
// if delete did not affect any rows, return a not found
if (deletedRows == 0) {
return notFound("Product not found");
}
// construct a HTTP 204 response
return new Response(null, { status: 204 });
}
Compiling the Spin Application
To build the application, use the following command:
$ spin build
The output from the above command will look similar to the following:
Building component hello-postgresql with `npm run build`
> hello-postgresql@1.0.0 build
> npx webpack --mode=production && npx mkdirp target && npx j2w -i dist.js -d combined-wit -n combined -o target/hello-postgresql.wasm
asset dist.js 22.4 KiB [compared for emit] [javascript module] (name: main)
orphan modules 52.7 KiB [orphan] 46 modules
runtime modules 396 bytes 2 modules
./src/spin.js + 15 modules 20.4 KiB [not cacheable] [built] [code generated]
webpack 5.97.1 compiled successfully in 104 ms
Using user provided wit in: combined-wit
Successfully written component
Finished building all Spin components
Running the Spin Application Locally
Let’s run the Spin application on your local machine, before we will deploy it to Fermyon Wasm Functions. Although you might be familiar with the spin up command already, we have to provide the connection string for our PostgreSQL database, by setting the pg_connection_string variable in advance of running spin up.
Environment variables prefixed with SPIN_VARIABLE_ will be accessible by your applications, if a corresponding variable is defined as part of the application manifest (spin.toml).
At the beginning of this tutorial, we added the pg_connection_string variable to the application manifest, meaning we could now follow the pattern, set the SPIN_VARIABLE_PG_CONNECTION_STRING to tell our application which connection string should be used and run the application with spin up:
$ SPIN_VARIABLE_PG_CONNECTION_STRING="<YOUR_CONNECTION_STRING>" spin up
Executing the command above will produce a similar output to the following:
Logging component stdio to ".spin/logs/"
Serving http://127.0.0.1:3000
Available Routes:
hello-postgresql: http://127.0.0.1:3000 (wildcard)
Use a tool like curl to send a GET request to the /products endpoint at http://localhost:3000 to retrieve the list of all products from the PostgreSQL database:
$ curl -iX GET http://localhost:3000/products
In addition to the response body (a JSON array containing all the products), you should see response headers printed to stdout similar to this:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
content-type: application/json
content-length: 326
date: Thu, 23 Jan 2025 08:55:21 GMT
[{"id":"f062dc2-bbf2-4c6c-8169-3511462cd54b","name":"Belt","price":14.99},{"id":"c01dce8a-3a50-4ef6-a0f1-7f9f48a238c8","name":"Hoodie with Logo","price":79.99},{"id":"660f8927-cdc1-44c7-bdd1-f4926dbd8445","name":"Plain Hoodie","price":42.99},{"id":"faac630e-a645-4459-9d7e-751df4016a6e","name":"V-Neck T-Shirt","price":19.99}]
Deploy to Fermyon Wasm Functions
To deploy the application to Fermyon Wasm Functions, use the spin aka deploy command. The actual connection string for accessing the PostgreSQL database will be passed to the command using the --variable flag:
$ spin aka deploy \
--variable pg_connection_string="<YOUR_POSTGRESQL_CONNECTION_STRING_HERE>"
The above deploy command will produce similar output to the following:
Name of new app: hello-postgresql
Creating new app hello-postgresql in account your-account
Note: If you would instead like to deploy to an existing app, cancel this deploy and link this workspace to the app with `spin aka app link`
OK to continue? yes
Workspace linked to app hello-postgresql
Waiting for app to be ready... ready
App Routes:
- hello-postgresql: https://ec8a19d8-6d10-4056-bb69-cc864306b489.aka.fermyon.tech (wildcard)
Finally, you can use curl to interact with the application you just deployed to Fermyon Wasm Functions. First, let’s send a GET request to the /products endpoint to retrieve a list of all products:
$ curl https://rust-pg-12345678.aka.fermyon.tech/products
You should now see a JSON array containing all products being rendered to your terminal as shown here:
[
{
"id": "6f062dc2-bbf2-4c6c-8169-3511462cd54b",
"name": "Belt",
"price": 14.99
},
{
"id": "c01dce8a-3a50-4ef6-a0f1-7f9f48a238c8",
"name": "Hoodie with Logo",
"price": 79.99
},
{
"id": "faac630e-a645-4459-9d7e-751df4016a6e",
"name": "V-Neck T-Shirt",
"price": 19.99
}
]
For demonstration purposes, let’s also add a new product to the database by sending a POST request to the /products endpoint:
$ curl -iX POST -H 'content-type: application/json' \
-d '{"name": "Plain Hoodie", "price": 42.99}' \
https://rust-pg-12345678.aka.fermyon.tech/products
Because we passed the -i flag to the curl command above, you should also see all response headers (including the HTTP status code) returned from our application running on Fermyon Wasm Functions:
HTTP/1.1 201 Created
content-type: application/json
location: /products/660f8927-cdc1-44c7-bdd1-f4926dbd8445
content-length: 81
date: Tue, 21 Jan 2025 09:36:24 GMT
{"id":"660f8927-cdc1-44c7-bdd1-f4926dbd8445","name":"Plain Hoodie","price":42.99}
Congratulations 🎉, you implemented a fully functional CRUD application and deployed it to Fermyon Wasm Functions using Spin and JavaScript.
